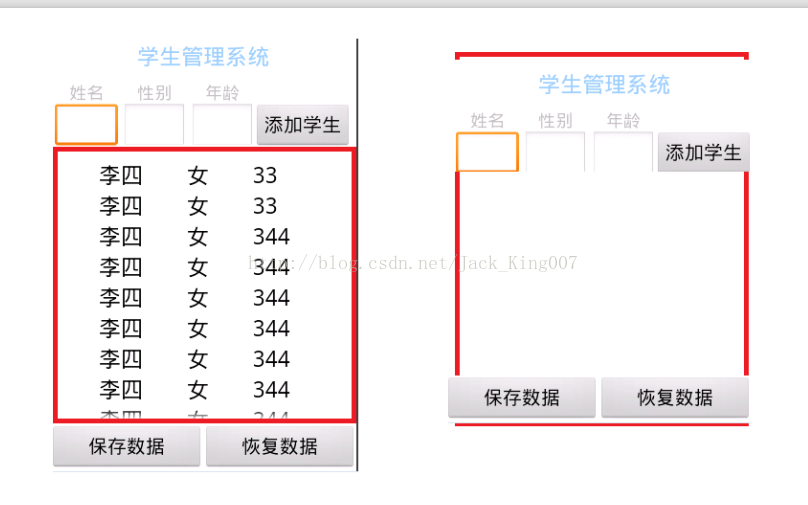
主界面应该就是这样的,大家可以动下你们的小脑袋,想下这个怎么写。
主界面 不难 最上方就是一个textview 显示内容
下方一个那个界面 用线性布局比较容易做,但是有点复杂,也是大部分人能想到的,但是从布局优化程度上来说,谷歌推荐相对布局,相对布局 先放三个Textview然后再用 属性below 将下三个Edittext 控制好 toleft属性 将button放置好。
ok 看着中间的布局 大家是不是马上想到了 listview ,不急 这个可以用 线性布局 可以显示 想不到吧
下面的就是一个button
布局如下
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="5dip"
android:text="学生管理系统"
android:textColor="#99CCFF"
android:textSize="23sp" />
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dip"
android:padding="5dip" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingLeft="15dip"
android:paddingRight="15dip"
android:text="姓名"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_sex"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dip"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_name"
android:paddingLeft="15dip"
android:paddingRight="15dip"
android:text="性别"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dip"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_sex"
android:paddingLeft="15dip"
android:paddingRight="15dip"
android:text="年龄"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/tv_name"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/tv_name"
android:layout_below="@id/tv_name"
android:singleLine="true" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_sex"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/tv_sex"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/tv_sex"
android:layout_below="@id/tv_sex"
android:singleLine="true" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/tv_age"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/tv_age"
android:layout_below="@id/tv_age"
android:inputType="number"
android:singleLine="true" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_add_student"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBaseline="@id/et_age"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/et_age"
android:text="添加学生"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</RelativeLayout>
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/ll_student_list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_margin="1dip"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="5dip" >
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dip"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_save"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="保存数据"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_restore"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="恢复数据"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>在回寝室的路上,我仔细想着我 一个APP 布局到实现的思路,还记我买彩票的时候,往往大部分的彩民,只会看别人的分析,然后跟着买,这样,亏得要比赢得多,为什么,这样你永远不知道为什么你会输,还不如自己分析各个球队的主力上场情况,受伤情况,加上庄家的盘口变化,就如自己总是拿着别人的封装好的东西,你永远只会是一个CV战士,万物其根本原理是一样,其实我又想到每个APP里面都会有广告栏,其实一个东西你想这永远都会很难,毕竟代码是一个一个敲出来的,不是想出来。
在想一个广告栏,无非就是三张图片不停的变化,用线程去发送消息更新, 这就牵扯到线程安全和ANC问题.....
回到这里,我想实现的无非就是添加数据 ,保存数据,回复数据,其实大家马上可以想到数据库,是的。但是这里不用。
让我们先来实现添加数据。
数据是从Edittext中获取到的 有Edittext的出现必然就会出现是否为空啦,Textutils 你值得拥有。 三个输入项都要用&&是否非空 。
好啦 这时候到了显示数据,大家都是在想用listview 显示数据 用adapter 但是其实用一个线性布局就可以实现了,布局直接AddView 就OK了 其实 这里大家可以思考下 既然线性布局可以这么简单的实现 那么为啥listview要那么复杂的实现。我相信谷歌工程师,进行大量的封装 和 继承,大家可以点开API看看,其实在安卓没有出现的时候,XML在java中是从来没有放过布局的,那时候java不擅长做GUI,只有才代码中实现.....
private void addStudent() {
String name = etName.getText().toString();
String sex = etSex.getText().toString();
String age = etAge.getText().toString();
if(!TextUtils.isEmpty(name)
&& !TextUtils.isEmpty(sex)
&& !TextUtils.isEmpty(age)) {
studentList.add(new Student(name, sex, Integer.valueOf(age)));
TextView childView = new TextView(this);
childView.setTextSize(23);
childView.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
childView.setText(" " + name + " " + sex + " " + age);
llStudentList.addView(childView);
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "请正确输入", 0).show();
}
}在刷新数据 不论是恢复数据,和保存数据,都是需要刷新界面,这个时候,一定会刷新数据的,SO,其实到后面相同代码就可以抽出来封装到一个类Or 方法
刷新数据:先要Remove 所有数据,清空,这个是必须 然后再取出你保存在list集合的数据,可以for循环去除,也可以用foreach 记住在循环里 顺便进行添加数据到线性布局中,
private void refreshStudentList() {
llStudentList.removeAllViews();
TextView childView;
for (Student student : studentList) {
childView = new TextView(this);
childView.setTextSize(23);
childView.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
childView.setText(" " + student.getName() + " " + student.getSex() + " " + student.getAge());
llStudentList.addView(childView);
}
}好啦 该到大问题的时候了,保存数据,其实保存数据可以 数据库,SP 保存文件,SD卡,但是其原理还是 java中的FIle操作,不过谷歌封装了,这里大家可以自己选择,
将list文件中的数据 去除 以xml形式保存在本地,这就是数据持久话的操作。 xml 拼装和解析 我就不讲了。
所有代码
package com.example.sp;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParser;
import org.xmlpull.v1.XmlSerializer;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.Xml;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private EditText etName;
private EditText etSex;
private EditText etAge;
private LinearLayout llStudentList;
private List<Student> studentList;
private String filePath;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
private void init() {
etName = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_name);
etSex = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_sex);
etAge = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_age);
llStudentList = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll_student_list);
findViewById(R.id.btn_save).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.btn_restore).setOnClickListener(this);
findViewById(R.id.btn_add_student).setOnClickListener(this);
studentList = new ArrayList<Student>();
filePath = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getPath() + "/student.xml";
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_save:
if(studentList.size() > 0) {
if(saveStudent2Local()) {
Toast.makeText(this, "保存成功", 0).show();
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "保存失败", 0).show();
}
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "当前没有数据", 0).show();
}
break;
case R.id.btn_restore:
if(restoreStudentFromLocal()) {
Toast.makeText(this, "恢复成功", 0).show();
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "恢复失败", 0).show();
}
break;
case R.id.btn_add_student:
addStudent();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
private boolean restoreStudentFromLocal() {
try {
XmlPullParser parser = Xml.newPullParser();
parser.setInput(new FileInputStream(filePath), "utf-8");
int eventType = parser.getEventType();
studentList.clear();
Student student = null;
String nodeName = null;
while(eventType != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
nodeName = parser.getName();
switch (eventType) {
case XmlPullParser.START_TAG:
if("student".equals(nodeName)) {
student = new Student();
} else if("name".equals(nodeName)) {
student.setName(parser.nextText());
} else if("sex".equals(nodeName)) {
student.setSex(parser.nextText());
} else if("age".equals(nodeName)) {
student.setAge(Integer.valueOf(parser.nextText()));
}
break;
case XmlPullParser.END_TAG:
if("student".equals(nodeName)) {
studentList.add(student);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
eventType = parser.next();
}
refreshStudentList();
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
private void refreshStudentList() {
llStudentList.removeAllViews();
TextView childView;
for (Student student : studentList) {
childView = new TextView(this);
childView.setTextSize(23);
childView.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
childView.setText(" " + student.getName() + " " + student.getSex() + " " + student.getAge());
llStudentList.addView(childView);
}
}
private boolean saveStudent2Local() {
try {
XmlSerializer serializer = Xml.newSerializer();
serializer.setOutput(new FileOutputStream(filePath), "utf-8");
serializer.startDocument("utf-8", true);
serializer.startTag(null, "infos");
for (Student stu : studentList) {
serializer.startTag(null, "student");
serializer.startTag(null, "name");
serializer.text(stu.getName());
serializer.endTag(null, "name");
serializer.startTag(null, "sex");
serializer.text(stu.getSex());
serializer.endTag(null, "sex");
serializer.startTag(null, "age");
serializer.text(String.valueOf(stu.getAge()));
serializer.endTag(null, "age");
serializer.endTag(null, "student");
}
serializer.endTag(null, "infos");
serializer.endDocument();
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
private void addStudent() {
String name = etName.getText().toString();
String sex = etSex.getText().toString();
String age = etAge.getText().toString();
if(!TextUtils.isEmpty(name)
&& !TextUtils.isEmpty(sex)
&& !TextUtils.isEmpty(age)) {
studentList.add(new Student(name, sex, Integer.valueOf(age)));
TextView childView = new TextView(this);
childView.setTextSize(23);
childView.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
childView.setText(" " + name + " " + sex + " " + age);
llStudentList.addView(childView);
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "请正确输入", 0).show();
}
}
}